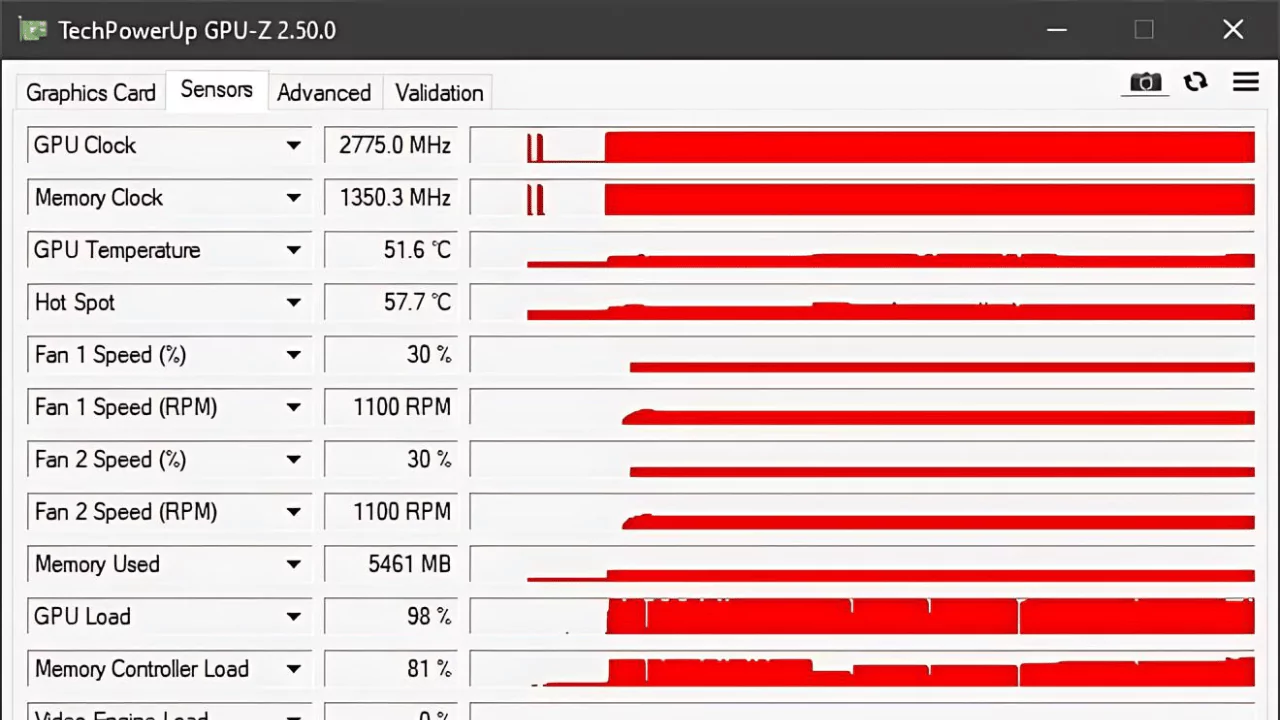
GPU Hotspot Temperature refers to the temperature measured by sensors within the SoC, indicating the hottest core’s temperature. Managed directly by the GPU BIOS, users cannot control it. The maximum allowed GPU Hotspot Temperature by NVIDIA before thermal throttling kicks in is 104.9°C, with throttling beginning at 105°C (According to the screenshot).
Defining GPU Hotspot Temperature
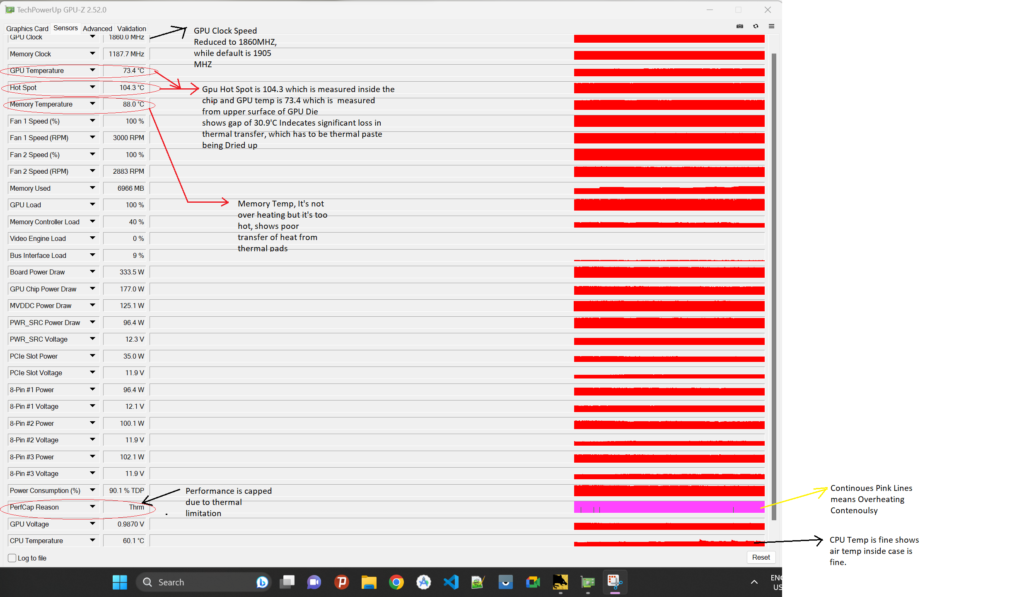
The term GPU hotspot temperature refers to the highest temperature reported by the sensors placed throughout a graphics card. Modern GPUs have multiple sensors that track temperature in different areas. The reading from the hottest sensor is known as the hotspot temperature.
Monitoring this temperature is crucial for maintaining optimal performance. If the hotspot temperature rises too high, it can lead to issues during demanding tasks like gaming or rendering. Keeping the GPU temperature in check ensures it runs smoothly and efficiently.
Factors That Affect GPU Hotspot Temperature
Several elements influence the GPU hotspot temperature.
Cooling Efficiency and Its Role
Cooling efficiency is a key factor in managing hotspot temperatures. Effective cooling systems help dissipate heat generated by the GPU. High-quality fans, heatsinks, and liquid cooling solutions help maintain lower temperatures. Poor airflow or blocked vents can lead to higher hotspot readings.
The Impact of Thermal Interface Material (TIM) Application
Thermal Interface Material plays an important role in heat transfer between the GPU die and its cooler. Proper application of TIM allows efficient heat transfer, lowering hotspot temperatures. Over time, TIM can dry out and become less effective. Regularly reapplying TIM can significantly improve thermal performance.
How Overclocking Affects Temperature
Overclocking increases the performance of a GPU by running it at higher speeds than its default settings. This process can generate more heat, leading to increased hotspot temperatures. Users who overclock must be mindful of their cooling solutions to prevent temperatures from reaching dangerous levels.
Why You Should Care About GPU Hotspot Temperature
Understanding GPU hotspot temperature is important for several reasons.
Effects on Performance
High hotspot temperatures can cause performance issues. When temperatures climb too high, the GPU may automatically reduce its speed to prevent overheating. This process, known as throttling, can result in lower frame rates and lag during gaming. Keeping hotspot temperatures in check ensures the GPU operates at peak performance.
Potential Damage to Hardware
Prolonged exposure to high hotspot temperatures can damage hardware components. Parts like the GPU die, memory chips, and voltage regulators are sensitive to heat. If temperatures stay too high for too long, it can lead to irreversible damage. Monitoring and managing hotspot temperatures can extend the lifespan of a graphics card.
Tips for Keeping Temperatures in Check
There are several strategies for maintaining safe hotspot temperatures.
- Improve Airflow: Ensure proper airflow within the PC case. Clean out dust and debris from fans and vents. Adding case fans can also improve airflow.
- Increase Fan Speed: Most graphics cards allow users to adjust fan speeds. Increasing the fan speed can help cool the GPU more effectively.
- Repaste the GPU: Over time, the thermal paste between the GPU and cooling unit can wear out. Replacing the thermal paste can greatly improve heat transfer.
- Limit Overclocking: If experiencing high hotspot temperatures, consider reducing or disabling overclocking. This can help lower heat output.
- Monitor Temperatures: Use monitoring software to keep track of both average and hotspot temperatures. Programs like HWMonitor or GPU-Z can provide real-time readings.
By being aware of GPU hotspot temperature and following these tips, users can enhance their gaming experience and prolong the life of their graphics hardware. Recognizing the signs of overheating and taking preventive measures will lead to better performance and system stability.