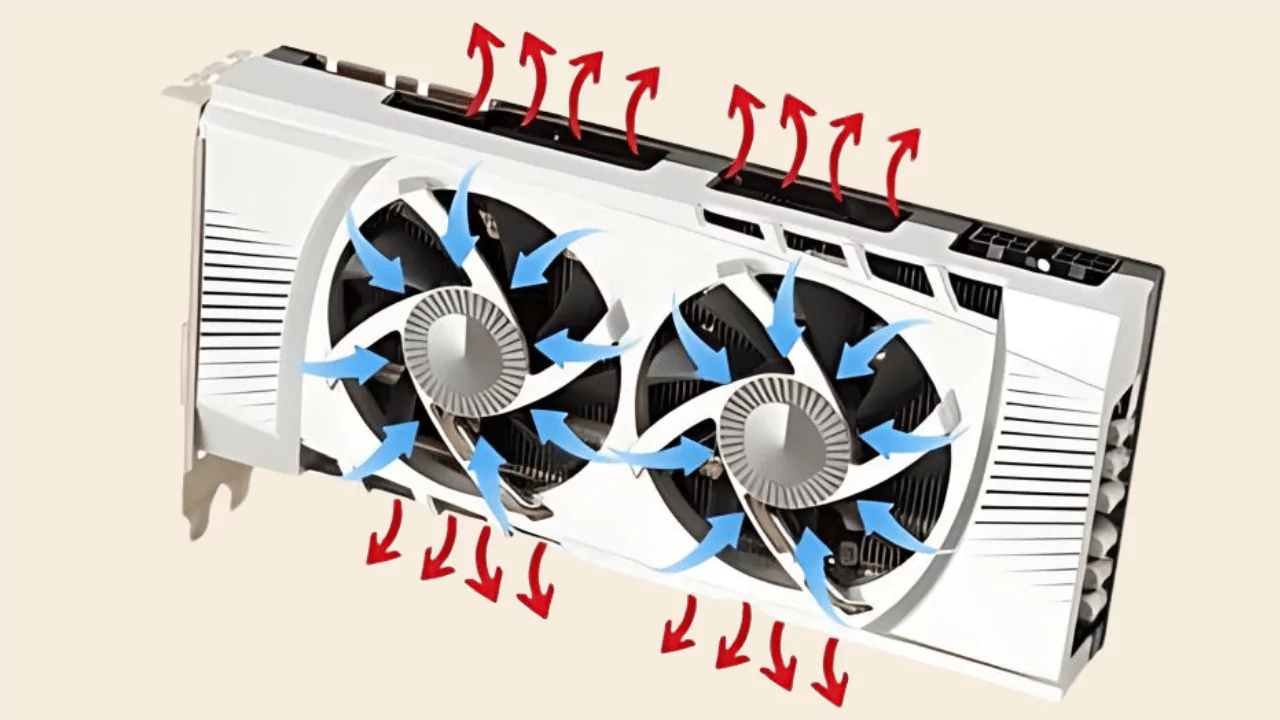
GPU fans typically blow air across the fins of a GPU to dissipate heat out of the side of the GPU and into the case. The direction of the airflow can be managed by mounting the fans facing downwards, which allows more air to pass across the GPU.
How does the direction of GPU fan airflow impact overall system cooling?
The direction of GPU fan airflow plays a key role in system cooling. When GPU fans blow air away from the card, they create a flow that affects the entire case. This airflow helps:
- Remove heat from other components
- Create positive air pressure inside the case
- Prevent dust buildup
Proper GPU fan direction works with case fans to create an efficient cooling system. Case fans usually bring cool air in from the front and bottom, while exhaust fans at the top and rear remove hot air. GPU fans complement this flow by pushing hot air towards the exhaust fans.
If GPU fans blow in the wrong direction, they can:
- Disrupt the case’s airflow
- Recirculate hot air
- Cause heat buildup around other components
This can lead to higher temperatures, reduced performance, and potential damage to hardware over time.
Can GPU fan direction be changed manually for better cooling performance?
In most cases, GPU fan direction cannot be changed manually. The fan design and mounting are fixed to blow air in the correct direction for optimal cooling. However, users can take steps to improve cooling performance:
- Adjust fan speed using software tools
- Clean dust from fans and heatsinks
- Improve case airflow with additional fans
- Use a custom GPU cooler (for advanced users)
Some aftermarket GPU coolers allow for fan replacement or repositioning. This can provide more control over airflow direction, but it requires technical skill and may void warranties.
What are the signs that GPU fans are blowing in the wrong direction?
While it’s rare for GPU fans to blow in the wrong direction, there are signs that indicate improper airflow:
- Higher than normal GPU temperatures
- Increased system temperatures
- Louder fan noise
- Reduced performance or instability
- Dust buildup on the GPU’s PCB or backplate
If you notice these issues, check the GPU fan operation. Look for obstructions or damage that might affect airflow. In some cases, a faulty fan might spin in the wrong direction, causing cooling problems.
How does the placement of a GPU within a case affect fan airflow direction?
GPU placement in a case can impact fan airflow effectiveness. Most cases are designed with GPUs installed horizontally in PCIe slots. This standard placement allows GPU fans to:
- Draw cool air from below the card
- Exhaust hot air through the top and rear
Some cases offer vertical GPU mounting options. While this can look appealing, it may affect airflow:
- Vertical mounting can limit the space between the GPU and side panel
- This restriction may reduce the fan’s ability to pull in cool air
- Hot air might recirculate instead of being expelled from the case
When choosing GPU placement, consider:
- Case design and airflow patterns
- Available space around the GPU
- Other component locations
Proper placement ensures GPU fans can operate effectively and contribute to overall system cooling.
Do different GPU models have varying default fan directions?
Most GPU models follow a standard fan direction, blowing air away from the card. However, cooling designs can vary between manufacturers and models:
- Reference designs: These usually use a blower-style fan that expels hot air directly out of the case through the GPU’s rear bracket.
- Custom designs: Aftermarket cards often use multiple fans that blow air across the heatsink. This air then exits through various points on the card and into the case.
- Hybrid designs: Some high-end GPUs combine traditional fans with liquid cooling, altering the airflow pattern.
While the basic principle of moving air away from the GPU remains consistent, different models achieve this in various ways:
- Single fan designs focus airflow in one direction
- Dual and triple fan setups create a wider spread of air movement
- Larger fans can move more air at lower speeds, reducing noise
When choosing a GPU, consider how its cooling design will work with your case layout and existing airflow patterns.